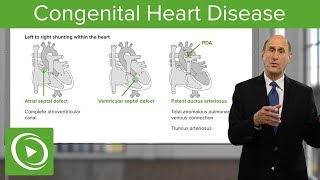
En este vídeo explico los principales mecanismos que demuestran la influencia del ejercicio físico sobre el estado de ánimo, incluyendo la mejora del metabolismo de la serotonina, opioides endógenos, cortisol y la conexión entre los músculos y el cerebro mediante la miokina irisina.
PARTES DEL VIDEO:
0:00 - INTRO
0:57 - La depresión es un trastorno biológico
3:01 - La Serotonina
5:32 - El Cortisol
8:25 - Los Opioides Endógenos
10:32 - La Miokina IRISINA
14:11 - Conclusión
BIBLIOGRAFIA:
1 Effects of exercise training on older patients with major depression
2 Comparative effectiveness of exercise, antidepressants and their combination in treating non-severe depression: a systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials
3 Antidepressant Drugs and Physical Activity: A Possible Synergism in the Treatment of Major Depression?
4 A Role for Branched-Chain Amino Acids in Reducing Central Fatigue. How to increase serotonin in the human brain without drugs
5 Can physical exercise modulate cortisol level in subjects with depression? A systematic review and meta-analysis
6 The effects of physical activity on cortisol and sleep: A systematic review and meta-analysis
7 Body temperature and analgesic effects of selective mu and kappa opioid receptor agonists microdialyzed into rat brain
8 Exercise plasma boosts memory and dampens brain inflammation via clusterin
9 Comparative efficacy and acceptability of 21 antidepressant drugs for the acute treatment of adults with major depressive disorder: a systematic review and network meta-analysis
10 The Effects of Acute Exercise on Mood, Cognition, Neurophysiology, and Neurochemical Pathways
11 Possible role of exercise therapy on depression: Effector neurotransmitters as key players
12 Endurance exercise increases skeletal muscle kynurenine aminotransferases and plasma kynurenic acid in humans
13 Exercise as a treatment for depression: A meta-analysis adjusting for publication bias
14 Covering the Role of PGC-1 in the Nervous System
PARTES DEL VIDEO:
0:00 - INTRO
0:57 - La depresión es un trastorno biológico
3:01 - La Serotonina
5:32 - El Cortisol
8:25 - Los Opioides Endógenos
10:32 - La Miokina IRISINA
14:11 - Conclusión
BIBLIOGRAFIA:
1 Effects of exercise training on older patients with major depression
2 Comparative effectiveness of exercise, antidepressants and their combination in treating non-severe depression: a systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials
3 Antidepressant Drugs and Physical Activity: A Possible Synergism in the Treatment of Major Depression?
4 A Role for Branched-Chain Amino Acids in Reducing Central Fatigue. How to increase serotonin in the human brain without drugs
5 Can physical exercise modulate cortisol level in subjects with depression? A systematic review and meta-analysis
6 The effects of physical activity on cortisol and sleep: A systematic review and meta-analysis
7 Body temperature and analgesic effects of selective mu and kappa opioid receptor agonists microdialyzed into rat brain
8 Exercise plasma boosts memory and dampens brain inflammation via clusterin
9 Comparative efficacy and acceptability of 21 antidepressant drugs for the acute treatment of adults with major depressive disorder: a systematic review and network meta-analysis
10 The Effects of Acute Exercise on Mood, Cognition, Neurophysiology, and Neurochemical Pathways
11 Possible role of exercise therapy on depression: Effector neurotransmitters as key players
12 Endurance exercise increases skeletal muscle kynurenine aminotransferases and plasma kynurenic acid in humans
13 Exercise as a treatment for depression: A meta-analysis adjusting for publication bias
14 Covering the Role of PGC-1 in the Nervous System
- Category
- Metabolism
Be the first to comment