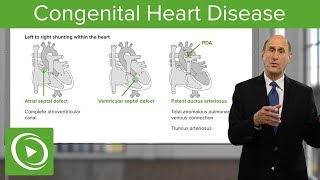
Cardiac arrest is a sudden and unexpected loss of heart function, breathing, and consciousness. It is a medical emergency that, if not treated immediately, usually results in death.
---
???? What Happens During Cardiac Arrest?
The heart suddenly stops beating effectively.
Blood stops flowing to the brain and other vital organs.
Breathing may stop within seconds.
The person collapses and becomes unresponsive.
---
⚠️ Signs and Symptoms
Sudden collapse
No pulse
No breathing
Loss of consciousness
Sometimes: chest pain, dizziness, palpitations, or shortness of breath before collapse
---
???? Causes
Heart conditions (most common): coronary artery disease, heart attack
Arrhythmias (e.g., ventricular fibrillation)
Cardiomyopathy
Electrolyte imbalances (e.g., low potassium or magnesium)
Severe blood loss or oxygen deficiency
Drug overdose or poisoning
---
???? Immediate Treatment (What to Do)
Call for emergency help immediately (e.g., 911).
1. Start CPR (Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation)
Push hard and fast in the center of the chest (100–120 compressions per minute).
If trained, provide rescue breaths.
2. Use an AED (Automated External Defibrillator)
If available, use as soon as possible.
It can analyze the heart rhythm and deliver a shock if needed.
---
???? Hospital Management
Advanced cardiac life support (ACLS)
Defibrillation
Oxygen and ventilation support
Medications (like epinephrine, amiodarone)
Identifying and treating the underlying cause
---
???? Survival and Prognosis
Time is critical. Each minute without CPR and defibrillation reduces survival by 7–10%.
With prompt treatment, survival is possible and may be followed by neurological recovery if the brain was not deprived of oxygen for too long.
---
Would you like:
An infographic for easy reference?
A deeper explanation of CPR steps?
Details on how cardiac arrest differs from a heart attack?
---
???? What Happens During Cardiac Arrest?
The heart suddenly stops beating effectively.
Blood stops flowing to the brain and other vital organs.
Breathing may stop within seconds.
The person collapses and becomes unresponsive.
---
⚠️ Signs and Symptoms
Sudden collapse
No pulse
No breathing
Loss of consciousness
Sometimes: chest pain, dizziness, palpitations, or shortness of breath before collapse
---
???? Causes
Heart conditions (most common): coronary artery disease, heart attack
Arrhythmias (e.g., ventricular fibrillation)
Cardiomyopathy
Electrolyte imbalances (e.g., low potassium or magnesium)
Severe blood loss or oxygen deficiency
Drug overdose or poisoning
---
???? Immediate Treatment (What to Do)
Call for emergency help immediately (e.g., 911).
1. Start CPR (Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation)
Push hard and fast in the center of the chest (100–120 compressions per minute).
If trained, provide rescue breaths.
2. Use an AED (Automated External Defibrillator)
If available, use as soon as possible.
It can analyze the heart rhythm and deliver a shock if needed.
---
???? Hospital Management
Advanced cardiac life support (ACLS)
Defibrillation
Oxygen and ventilation support
Medications (like epinephrine, amiodarone)
Identifying and treating the underlying cause
---
???? Survival and Prognosis
Time is critical. Each minute without CPR and defibrillation reduces survival by 7–10%.
With prompt treatment, survival is possible and may be followed by neurological recovery if the brain was not deprived of oxygen for too long.
---
Would you like:
An infographic for easy reference?
A deeper explanation of CPR steps?
Details on how cardiac arrest differs from a heart attack?
- Category
- Cardiology
Be the first to comment